Understanding why your female dog engages in humping behavior, particularly with her toys, can be puzzling for many pet owners. This article will help you to decipher the reasons behind this behavior and provide advice, based on my own first hand experience, for managing it effectively. Despite being a topic that’s often associated with male dogs, female dogs also exhibit this behavior for various reasons that extend beyond their sexual impulses.


Understanding Humping Behavior in Female Dogs
The reasons for your dog’s humping behavior may vary but most commonly, your female canine can be going through a period of heat which may result in hormonal fluctuations that can lead to humping behavior. Still, in other cases, reasons may include underlying medical conditions, excitement, over-stimulation anxiety, or just their need to assert dominance. These behaviors are natural and manageable, so you don’t have to be overly concerned about your pup.
The Basics of Canine Humping
What is humping?
To understand their behavior, you need to know the action and where it originates. Humping, or mounting, is a physical action often characterized by a dog grabbing a toy, another dog, or even a human’s leg and making thrusting movements. If you’ve been wondering what your dog is doing on your leg, this is it.
Common Misconceptions
While it’s commonly associated with sexual behavior, humping can signify many other things in the canine world. Multiple reasons can result in your dog engaging in a humping behavior, and the reasons behind it are as follows:
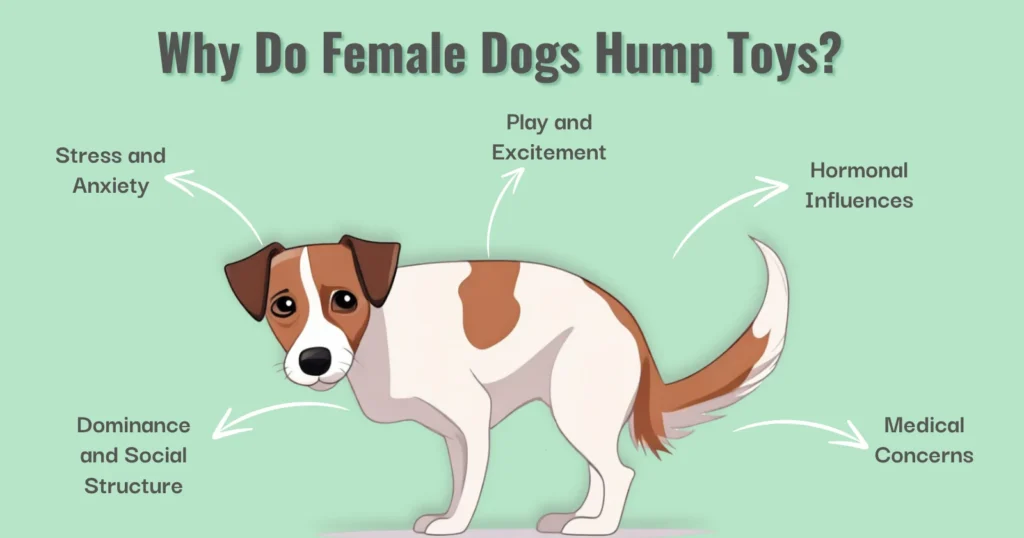
5 Reasons Behind Female Dog Humping
1- Hormonal Influences
- Estrus Cycle: Female dogs in heat may hump more frequently due to the hormonal changes they experience.
- Spayed Females: Even after being spayed, some females may continue to hump due to residual hormonal influences.


2- Play and Excitement
- Play Behavior: Dogs, especially younger ones, may hump their toys during play as a way of expressing excitement or practicing social skills. If your little pup can not wait to play with you they may be engaging in this action.
- Over-stimulation: High levels of excitement can trigger humping behavior as a response to sensory overload.
3-Dominance and Social Structure
- Establishing Hierarchy: In multi-dog households, a female dog might hump to assert dominance or control over her toys or other dogs. In such a situation, you may want to teach her how to share her toys. After all, we want our furry friends to get along with eachother not engage in fights.
- Social Signals: Humping can also be a way for dogs to navigate social interactions, test boundaries, and express themselves.
4- Stress and Anxiety
- Stress Relief: For some dogs, humping can be a coping mechanism to relieve stress or anxiety. The occurrence is common in male dogs as well. Some puppies will chew aggressively and others might just hump their toys.
- Compulsive Behavior: In some instances, repetitive humping may evolve into a compulsive habit if it becomes a primary method for dealing with stress. So take note of when your dog exhibit’s these behaviors and address them there and then.
5- Medical Concerns
- Urinary Tract Infections: Irritation in the urinary tract may lead to humping as a form of relief. Yes, dogs can get UTI if they are poor on hygiene, therefore make sure to give them a clean environment and give them frequent baths.
- Skin Allergies: Allergies causing itchiness in the genital area can sometimes trigger humping behavior. It could be some thing he picked up in the park or while chasing out an infected animal in the garden.
NOTE: Disinfect your dog toys before letting your puppy play with them to avoid infections.


Addressing Humping Behavior in Female Dogs
Training and Behavior Modification
Redirect Attention, when your dog starts to hump, redirect her focus to a different, acceptable activity, I usually resort to playing fetch. I have a friend who had a similar problem with her dog; her coping mechanism was taking her dog out to the park for a couple of hours every day to make use of her pent-up energy.
Use of commands like “stop” or “leave it” to control humping behavior effectively.
Environmental Management
Routine Exercise and regular physical activity can help manage excess energy that might otherwise be channeled into humping. Addressing mental Stimulation: engage your dog in interactive toys and puzzles to keep her mind stimulated and prevent boredom. Our furry friends tend to get bored quite easily therefore you need to keep them occupied.


Socialization and Play
Proper socialization is crucial for your dog; just like humans, they need to socialize. Introduce your dog to various environments and other dogs under controlled conditions to improve her social skills.
Monitor playtime and ensure that play with other dogs is healthy, and intervene if humping occurs frequently to prevent it from becoming a habit.
Seeking Professional Help
Regular veterinary examination will help you rule out any underlying medical issues contributing to the behavior. You can always resort to professional training. Consider hiring a dog behaviorist or trainer if the humping is persistent and difficult to manage. Professionals take charge in such situations because it can get overwhelming and frustrating for you and your pet.
Managing Hormonal Influences
Spaying your dog, if not already done, spaying can reduce the hormonal drive to hump, especially if the behavior is linked to the estrus cycle. Hormonal therapies are proven beneficial in some cases; veterinarians may recommend hormonal treatments to manage behavior under strict medical supervision.
While the sight of your female dog humping her toys might initially cause concern or embarrassment, understanding the multitude of reasons behind this behavior can help in addressing it appropriately. Whether driven by hormonal changes, excitement, dominance, stress, or even medical issues, recognizing the root cause is the first step towards effectively managing the behavior. By implementing training strategies, ensuring proper Exercise and mental Stimulation, and consulting with professionals when necessary, you can control this behavior and maintain a happy, healthy relationship with your dog.